Cone Calculator
Cone Shape
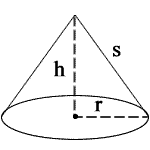
r = radius
h = height
s = slant height
V = volume
L = lateral surface area
B = base surface area
A = total surface area
θ = half-angle or apex angle of the full cone between the center axis and any side, in degrees
φ = 2θ = aperture or opening angle or vertex angle of the full cone between opposite sides, in degrees
β = base angle of the cone, in degrees
π = pi = 3.1415926535898
√ = square root
Calculator Use
This online calculator will calculate the various properties of a right circular cone given any 2 known variables. The term "circular" clarifies this shape as a pyramid with a circular cross section. The term "right" means that the vertex of the cone is centered above the base. Using the term "cone" by itself often commonly means a right circular cone.
Units: Note that units are shown for convenience but do not affect the calculations. The units are in place to give an indication of the order of the results such as ft, ft2 or ft3. For example, if you are starting with mm and you know r and h in mm, your calculations will result with s in mm, V in mm3, L in mm2, B in mm2 and A in mm2.
Below are the standard formulas for a cone. Calculations are based on algebraic manipulation of these standard formulas.
Circular Cone Formulas in terms of radius r and height h:
- Volume of a cone:
- V = (1/3)πr2h
- Slant height of a cone:
- s = √(r2 + h2)
- Lateral surface area of a cone:
- L = πrs = πr√(r2 + h2)
- Base surface area of a cone (a circle):
- B = πr2
- Total surface area of a cone:
- A = L + B = πrs + πr2 = πr(s + r) = πr(r + √(r2 + h2))
Circular Cone Calculations:
Use the following additional formulas along with the formulas above.
- Given radius and height calculate the slant height, volume, lateral surface area and total surface area.
Given r, h find s, V, L, A- use the formulas above
- Given radius and slant height calculate the height, volume, lateral surface area and total surface area.
Given r, s find h, V, L, A- h = √(s2 - r2)
- Given radius and volume calculate the height, slant height, lateral surface area and total surface area.
Given r, V find h, s, L, A- h = (3 * v) / (πr2)
- Given radius and lateral surface area calculate the height, slant height, volume and total surface area.
Given r, L find h, s, V, A- s = L / (πr)
- h = √(s2 - r2)
- Given radius and total surface area calculate the height, slant height, volume and lateral surface area.
Given r, A find h, s, V, L- s = [A - (πr2)] / (πr)
- h = √(s2 - r2)
- Given height and slant height calculate the radius, volume, lateral surface area and total surface area.
Given h, s find r, V, L, A- r = √(s2 - h2)
- Given height and volume calculate the radius, slant height, lateral surface area and total surface area.
Given h, V find r, s, L, A- r = √[ (3 * v) / (π * h) ]
- Given slant height and lateral surface area calculate the radius, height, volume, and total surface area.
Given s, L find r, h, V, A- r = L / (π * s)
- h = √(s2 - r2)
How to Calculate Cone Angles
If you look straight on to a full cone in two dimensions you will see an isosceles triangle. If you draw the height line from the center of the apex down to bisect the base you will get two right triangles formed by the height h, the radius r on the bottom, and the side s. It can be shown that the angle at the top of the right triangle, called the half-angle, is given by θ = arctan(r/h). If you know θ, and you know you have one right angle at 90°, then you can calculate the third, base angle β = 180 - 90 - θ.
References
Weisstein, Eric W. "Cone." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource.
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Cone.html